There are several strategies available, and choosing the right one depends on your financial goals, risk tolerance, and time commitment. Common strategies include:
Buy and Hold: Purchase a property to rent out long-term, generating steady income and appreciation.
Fix and Flip: Buy undervalued properties, renovate them, and sell for a profit. This requires capital and project management skills.
House Hacking: Live in part of the property (like a duplex) and rent out the rest to offset your mortgage.
Short-Term Rentals: Use platforms like Airbnb to generate income from vacation rentals, which can be lucrative but require active management.
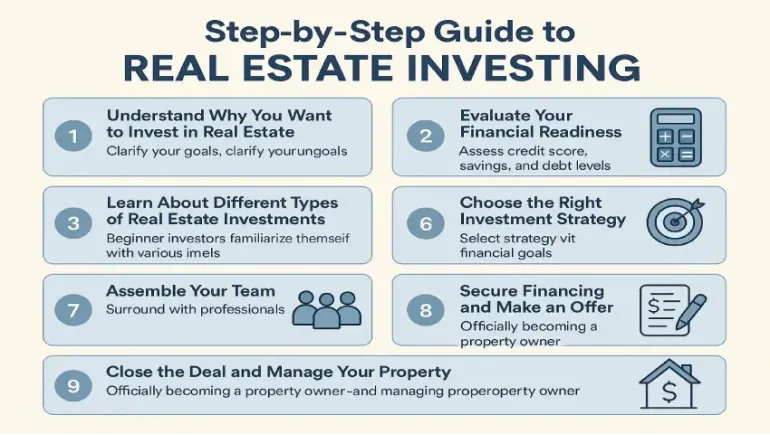
Step 6: Assemble Your Team
Real estate investing is a team sport. Surround yourself with professionals: a real estate agent experienced with investors, a lender or mortgage broker, a property inspector, a reliable contractor, and possibly a property manager. These experts can help you avoid costly mistakes and guide you through complex transactions. You’ll also want to consult an accountant or tax advisor to understand how property income, depreciation, and expenses impact your taxes.
Step 7: Run the Numbers
Always evaluate the financials before buying a property. Consider:
Cash Flow: Monthly rental income minus all expenses (mortgage, taxes, insurance, maintenance).
Cap Rate: Net operating income divided by the property’s purchase price.
ROI (Return on Investment): Total returns compared to your investment.
Make sure the deal makes sense on paper before you move forward. Being emotionally attached to a property can lead to poor decisions—always treat it as a business.
Step 8: Secure Financing and Make an Offer
Once you’ve found a property that checks all the boxes, get pre-approved by a lender and make a competitive offer. Be prepared for negotiations and inspections. A thorough inspection can reveal issues that might affect your return on investment or give you leverage to lower the price. If financing is a challenge, consider creative solutions like seller financing, partnerships, or using a HELOC (Home Equity Line of Credit) if you already own a home.
Step 9: Close the Deal and Manage Your Property
After your offer is accepted, you’ll go through closing—signing documents, transferring funds, and officially becoming a property owner. From there, the work begins. If you’re managing the property yourself, be prepared to handle tenant screening, rent collection, and maintenance. Alternatively, a property manager can take care of this for a fee (typically 8–12% of monthly rent). Effective property management is the key to long-term success. Keep good records, stay on top of maintenance, and treat your tenants with respect.
Real estate investing can be a powerful wealth-building tool, but success doesn’t happen overnight. Take the time to educate yourself, build a strong team, and be diligent in your research. The more prepared you are, the smoother your journey will be—and the greater your long-term rewards. Whether you're aiming for passive income or financial freedom, taking that first step into real estate could be one of the smartest moves you ever make.



-112x63.27.webp)




-132x74.57.webp)



Comments
There are no comments for this Article.